
"The anti-human polyclonal capture reagents are some of the most robust reagents I have used in my biophysical and biochemical studies so far. Overall, the anti-Fc reagents regardless of the host or capturing species provides a robust capturing ability with minimum cross-reactivity to other species." Full review.
Rupesh Nanjunda,Rating: 5.0

Jackson ImmunoResearch Mouse Monoclonal Anti-Human IgE antibodies are the latest addition to our suite of products suitable for diagnostics research and development. Specific for Human IgE antibodies, they complement our existing Anti-Human IgG, IgM, and IgA antibodies. Anti-Human IgE is available conjugated to a select range of reporter molecules, including Alkaline Phosphatase and Biotin enabling excellent sensitivity.
Jackson ImmunoResearch Anti-Human IgE antibodies are available in two different clones ( ME.114 and 10A10) and are both mouse-derived monoclonal antibodies with reactivity to human E class immunoglobulins and are epsilon (ε) chain specific.
Jackson immunoResearch Mouse Anti-Human IgE (clone number ME.114) (209-002-241) is available conjugated to a range of reporter molecules and is suitable to detect human IgE by a variety of techniques, including ELISA (Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay), Lateral flow immunoassay (LFIA), flow cytometry, Western blot, and CLIA (Chemiluminescent immunoassay).
Jackson ImmunoResearch Mouse Anti-Human IgE (clone number 10A10) (209-002-244) is available unconjugated and is designed to be used as a capture antibody in conjunction with a conjugated Anti-Human IgE antibody (clone number ME.114) in sandwich format assays.
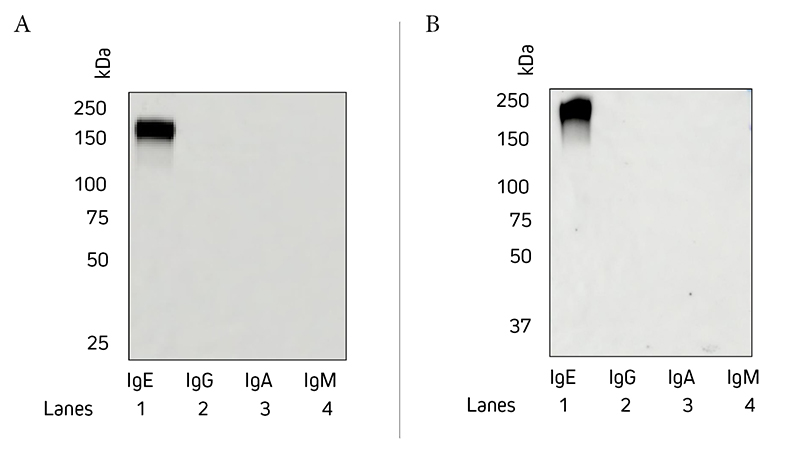
Jackson ImmunoResearch Anti-Human IgE epsilon (ε) chain specific antibodies have been tested by ELISA and show minimal cross-reactivity to human IgG, IgM, or IgA. Figure 1 is a Western blot that demonstrates the specificity of Jackson ImmunoResearch Anti-Human IgE antibodies (clones ME.114 and 10A10), showing no detection of other immunoglobulin classes. We have not tested if this antibody will detect immunoglobulins from other species.
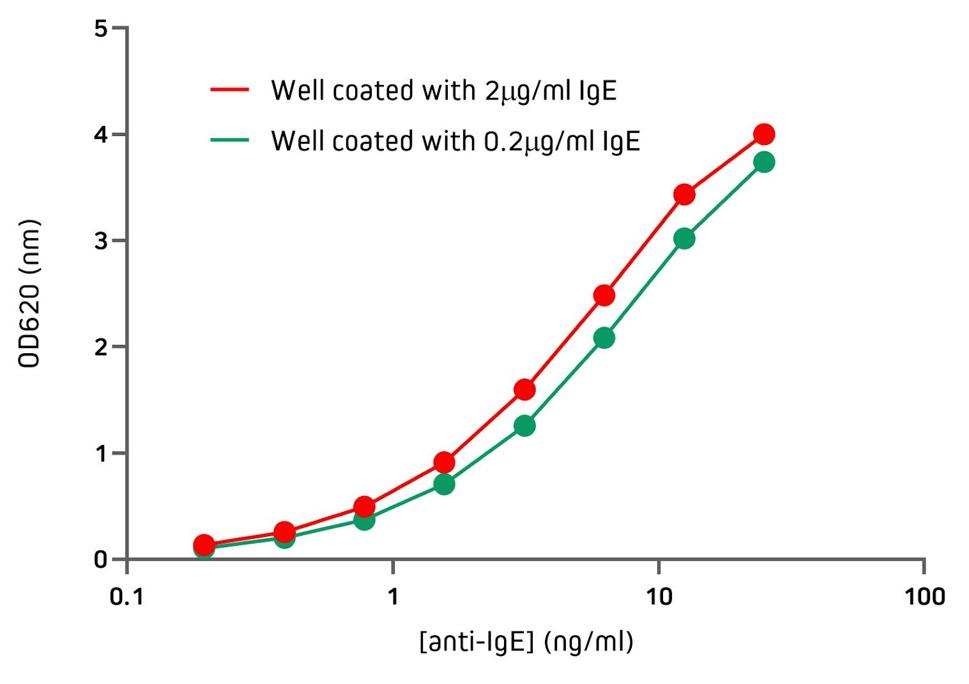
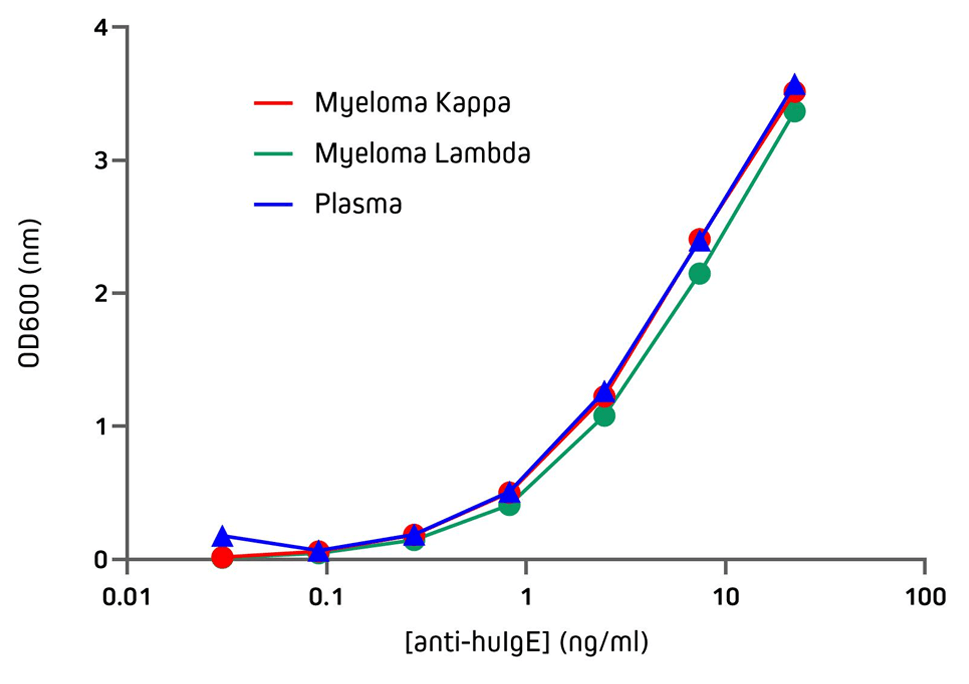
Jackson ImmunoResearch Anti-Human IgE antibodies can be used to detect human IgE from various sources with excellent sensitivity. Figure 3 demonstrates the sensitivity of Jackson ImmunoResearch Anti-Human IgE (clone number ME.114) when used in an indirect ELISA, showing its ability to detect IgE coating the wells at two different concentrations. Figure 4 demonstrates the sensitivity of Jackson ImmunoResearch Anti-Human IgE (clone number ME.114) when used in an indirect ELISA to detect IgE purified from different myeloma and plasma sources.
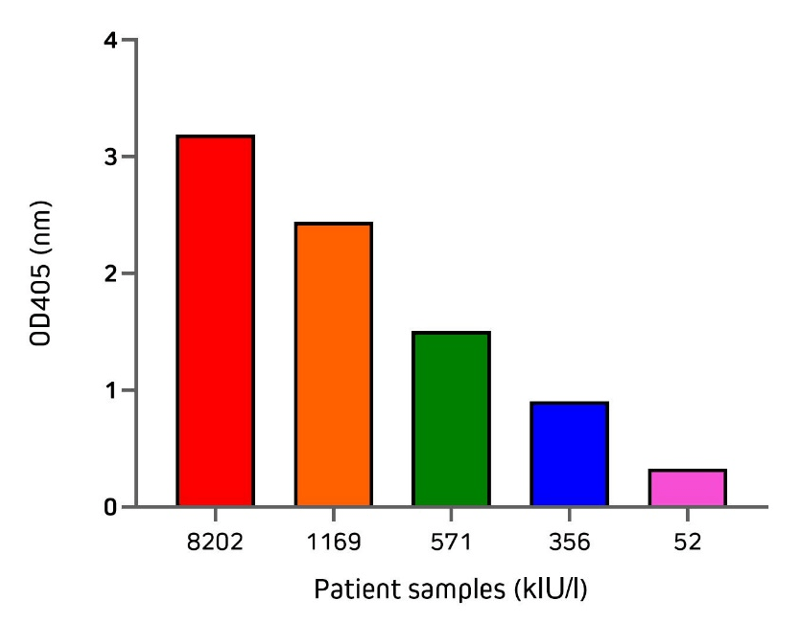
Jackson ImmunoResearch Anti-Human IgE offers excellent sensitivity when used in a sandwich ELISA with its capture partner antibody. Two different monoclonal antibodies may be used in a pair for capture and detection. In this format, use unconjugated Anti-Human IgE (clone 10A10 209-002-244) as your coating antibody before blocking with Bovine Serum Albumin (IgG-Free, Protease-Free 001-000-161). Following washing, incubate with your diluted sample. For the detection step, use a conjugated Anti-Human IgE antibody, such as Alkaline Phosphatase Anti-Human IgE (209-052-241) or Peroxidase Anti-Human IgE (209-032-241), followed by the appropriate substrate or visualization technique. Figure 5 illustrates the application of the direct sandwich assay to validate the quantification of total IgE from patient samples using unconjugated Anti-Human IgE in partnership with an alkaline phosphatase conjugated detection antibody. Total IgE (kIU/l) in patient samples used in this experiment were previously measured by the Roche Cobas Total IgE assay. These results are displayed on the x-axis of Figure 5.
The dilution factors suggested in the following table are presented as ranges because the optimal dilution is a function of many factors, such as antigen density, permeability, etc. The optimal working dilution should be determined empirically for each application.
| Application | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Conjugate | ELISA | Western Blots* | Flow Cytometry |
| Unconjugated | 10-20 µg/ml | ||
| FITC | 1:50-1:200 | ||
| R-PE | 1:50-1:200 | ||
| Horseradish Peroxidase | 1:5,000-1:100,000 | 1:5,000-1:100,000 (non-ECL) 1:10,000-1:200,000 (ECL) |
|
| Alkaline Phosphatase | 1:5,000-1:50,000 | 1:5,000-1:50,000 | |
| Biotin-SP (using Fluorophore-Conjugated Streptavidin) | 1:200-1:1,000 | ||
| Biotin-SP (using enzyme-Conjugated Streptavidin) | 1:20,000-1:400,000 | 1:20,000-1:400,000 | |
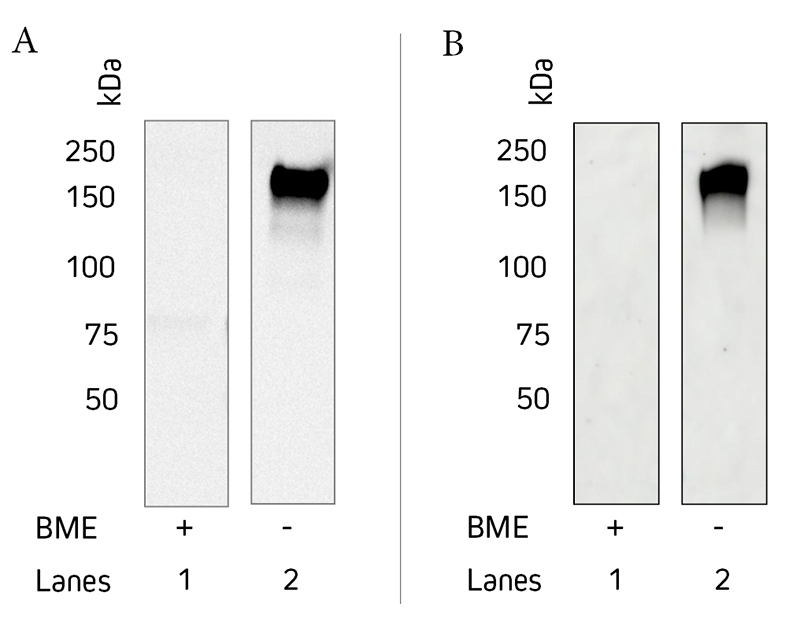
* Please note that this antibody will give a weaker signal when detecting reduced protein and therefore is not recommended for applications where detection of reduced IgE is required by western blot.