Colorimetric detection is an economical and simple method for the detection of analyte when Western blotting. Enzyme reporters conjugated to secondary antibodies react with a chromogenic substrate to generate a visually detectable signal, thus identifying the presence of the protein of interest directly on the blotting membrane.
Western blotting with colorimetric detection uses a secondary antibody conjugated to an enzyme reporter molecule which catalyzes the conversion of a soluble chromogenic substrate to a colored insoluble product. This product precipitates onto the blotting membrane to produce colored bands which can be seen by eye, identifying the protein of interest. Colorimetric signal detection is a useful method for general lab use with low set up costs, as no special equipment is required to visualize the signal.
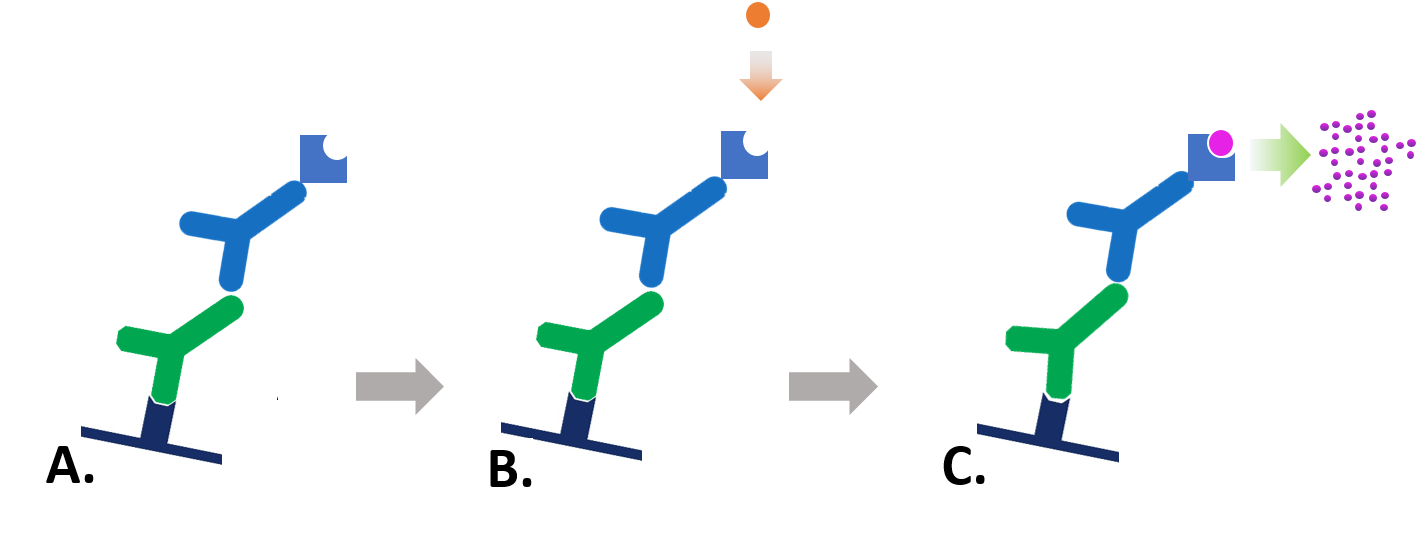
Figure 1: Indirect colorimetric detection. A. Enzyme-conjugated secondary antibody is bound to primary antibody at protein of interest. B. Substrate is added to antibody-antigen complex. C. Enzyme reacts with substrate, forming a detectable colored product.
Developing the blot is simple: the membrane is incubated with the chromogenic substrate until the required level of signal is developed, then the substrate is simply washed away. This stops the enzymatic reaction and halts the blot from developing further. Colorimetric detection is easy and quick to perform, offering greater flexibility for optimization compared to chemiluminescent or fluorescent systems. However, the immobilized precipitate does not lend itself to stripping and reprobing of the membrane, making multiple probing with additional antibodies unreliable.
Colorimetric Western blotting can have high sensitivity, but prolonged incubation leads to increased background signal which may obscure signal from the protein of interest. Therefore, colorimetric detection may be unsuitable for low abundance proteins. However, when the protein is known to be abundant or the method has been optimized, the simplicity and low cost make colorimetric detection attractive. There are a variety of substrates available which produce a range of colored precipitates, each offering different sensitivity.
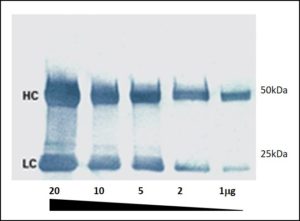
Figure 2: A colorimetric Western blot. Heavy (HC 50 kDa) and light (LC 25 kDa) chains of reduced and SDS-denatured mouse IgG were separated by SDS-PAGE and detected on Western blots using Peroxidase-Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) and visualized with TMB chromogenic substrate.
References:
Alberts B et al (1994) Molecular biology of the Cell. 3rd Ed. Garland press. London
Kalyuzhny A (2016) Immunohistochemistry – Essential Elements and Beyond. Springer International Publishing Switzerland.
Roitt et al (2005) Immunology. 6th Ed. Mosby. Spain


