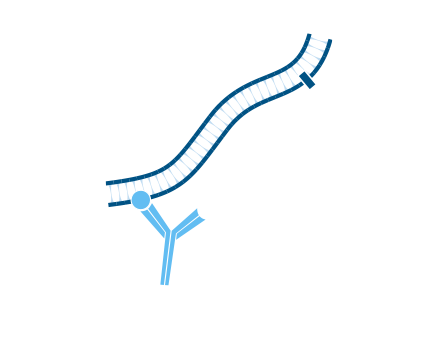
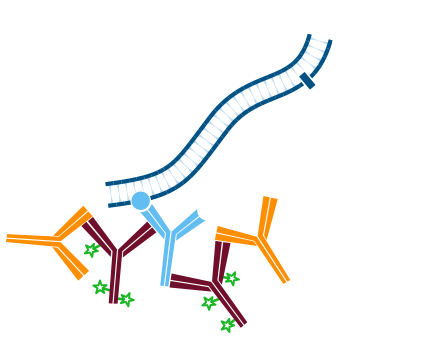
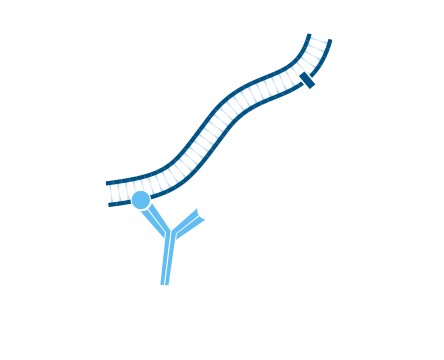
Step 1. After blocking with normal serum, incubate with the first primary antibody, in this example Rabbit Anti-Antigen X. Wash.
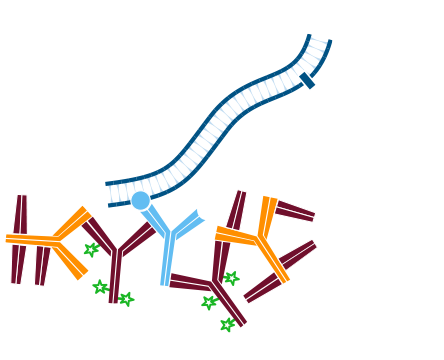
Step 2. Incubate with conjugated secondary antibody, in this example Alexa Fluor® 488-Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) (min X Hu, Ms, Rat Sr Prot). Wash.
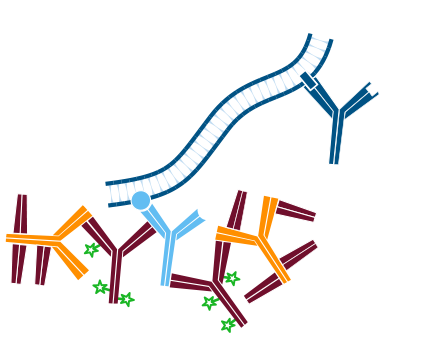
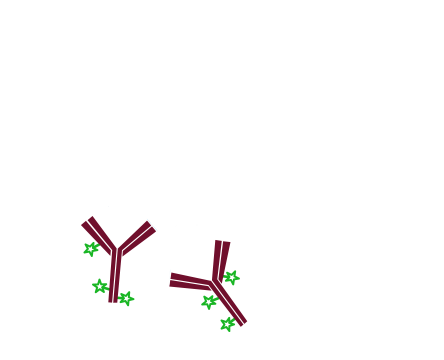
Step 3. Incubate with normal serum from the same host species as the primary antibodies, in this example normal rabbit serum. The purpose of this step is to saturate open binding sites on the first secondary antibody with IgG so that they cannot capture the second primary antibody. Wash.
Step 4. Incubate with an excess of unconjugated Fab antibody against the host species of the primary antibodies, in this example Fab Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L). The host species of the Fab antibody should be the same as the host species of the conjugated secondary antibody. This step covers the rabbit IgG so that the second secondary antibody will not bind to it. Wash.
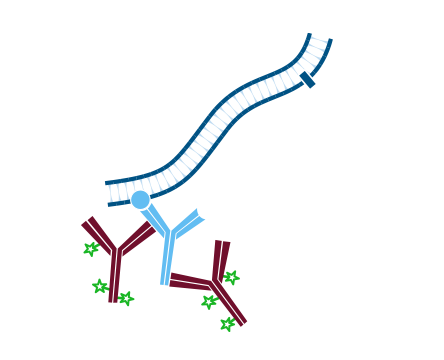
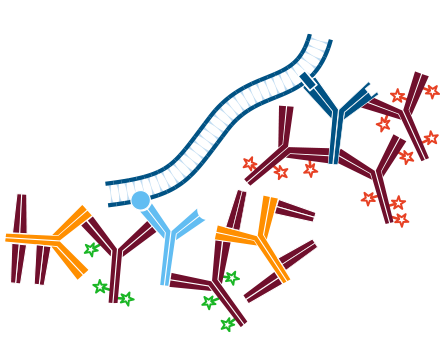
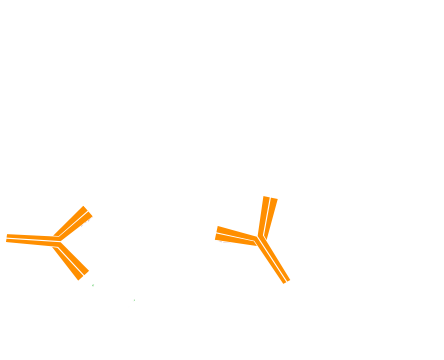
Step 5. Incubate with the second primary antibody, in this example Rabbit Anti-Antigen Y. Wash.
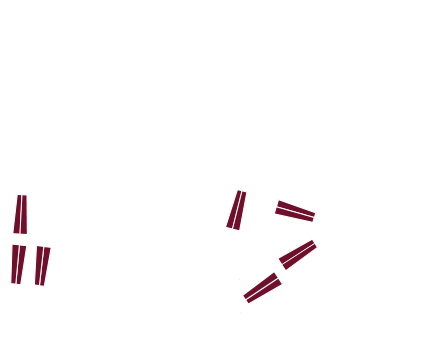
Step 6. Incubate with the same secondary antibody as used in step 2, conjugated to a different probe, in this example Rhodamine Red™‑X-Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) (min X Hu, Ms, Rat Sr Prot). Wash.